Import and export Airflow connections and variables
After you create connections and variables in an Airflow environment, you might want to move export and import them between environments for any of the following reasons:
- You are launching a production Airflow environment on Astro based on a locally running Airflow environment.
- You need to replicate a production Airflow environment on your local machine.
- Your team is migrating old Airflow environments to a new location.
Based on the management strategy for your connections and variables, their storage location will vary. Use this document to learn how to export and import them from one environment to another.
If you use the Astro Environment Manager to create connections, instead of importing and exporting connections from Airflow, you can configure the CLI to automatically retrieve connection details from Astro when you're working locally. See Work locally with Airflow connections hosted on Astro to set up this configuration and learn more about how Astro stores and syncs connection information.
From the Airflow UI and metadata database
When you use the Airflow UI to store your Airflow connections and variables, they are stored in Airflow's metadata database. If your variables are stored in Airflow's metadata database, you can use the Airflow UI to import and export them in bulk.
Using the Airflow UI
To export variables from a local Airflow environment or Astro Deployment, complete the following steps:
-
In the Airflow UI, go to Admin > Variables.
-
Select the variables you want to export, then click Export in the Actions dropdown menu.
The selected variables are exported to your local machine in a file named
variables.json.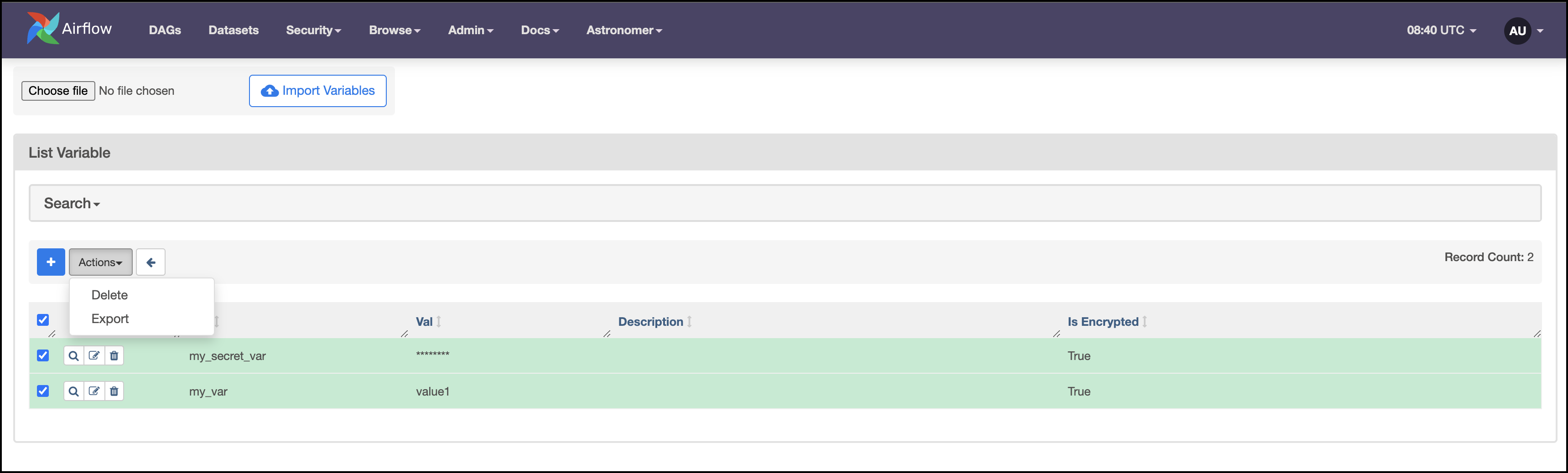
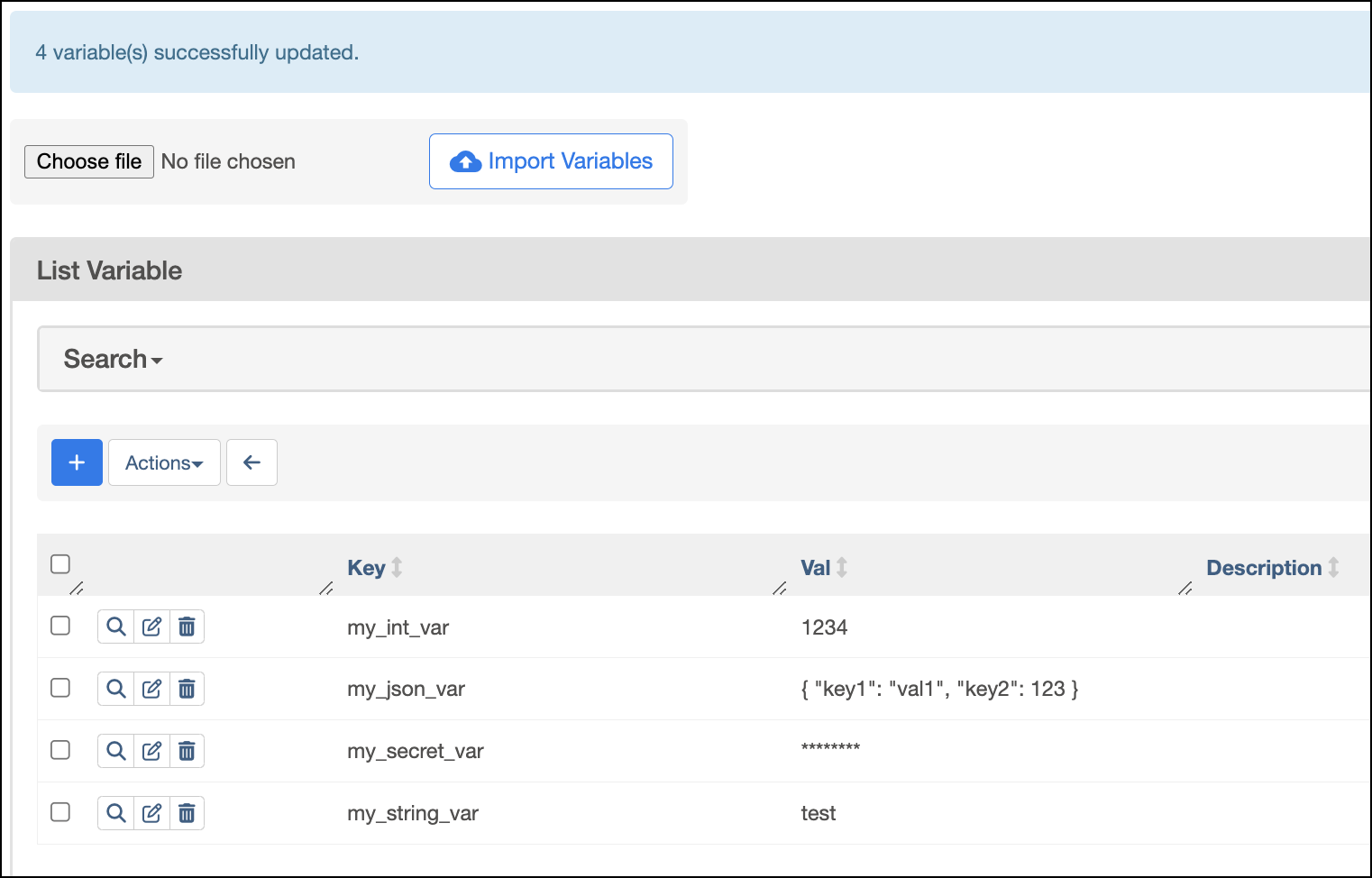
To import variables to a local Airflow environment or Astro Deployment from a json file, complete the following steps:
-
Either create a new
jsonfile with environment variables or follow the previous steps to export ajsonfile from an existing Airflow environment. Yourjsonfile should look similar to the following:
{
"my_string_var": "test",
"my_int_var": 1234,
"my_secret_var": "my_secret",
"my_json_var": {
"key1": "val1",
"key2": 123
}
} -
In the Airflow UI, go to Admin > Variables.
-
Click Choose file and select the file containing your environment variables. Then, click Import Variables.
After the variables are updated, the UI will show a confirmation message.
For security reasons, you can't bulk import or export connections from the Airflow UI.
Using the Astro CLI (Local environments only)
Use astro dev object export, astro dev object import, and astro dev run to import and export connections and variables from a local Airflow environment to various formats. For example:
-
To export all Airflow objects including connections, variables, and pools to your Astro project
.envfile in a URI format, run:astro dev object export --env-export -
To print only your connections connections in JSON format to STDOUT, run:
astro dev run connections export - --file-format=env --serialization-format=json -
To import all Airflow objects from a file named
myairflowobjects.yamlto a locally running Airflow environment, run:astro dev object import --settings-file="myairflowobjects.yaml"
From a secrets backend
If you use a secrets backend to store connections and variables, you need to use your secrets backend's API to manage connections and variables between environments. Note that importing/exporting from a secrets backend is necessary only in rare circumstances, such as when:
- You want to migrate your secrets backend to a different account.
- You want to use your secrets as a reference for another Deployment and then customize it. Astronomer recommends maintaining separate
developmentandproductionsecrets backend. - You want to migrate to a different cloud provider.
Refer to your secrets backend provider's documentation to learn how to manage resources using API calls:
- Google secret manager's Python SDK and REST API reference.
- AWS secret manager's Python SDK and other SDKs.
- Azure key vault's SDK and API reference.
- Hashicorp Vault's Python SDK
To set up a secrets backend on Astro, see configure secrets backend.
From environment variables
If you use an .env file to manage your connections and variables as environment variables in a local Astro project, you can import your Airflow objects to another local Airflow Astro project by copying the .env file into the destination project.
The .env file is not pushed to your Deployment when you run astro deploy. However, you can use Astro CLI commands to import the contents of your .env file to an Astro Deployment using astro deployment commands.
If your connections and variables are stored in a local Airflow metadata database, you can also export these to a .env file and then import them to an Astro Deployment as environment variables.
-
To export all Airflow objects from your local Airflow environment, including connections and variables, to an
.envfile in URI format, run:astro dev object export --env-export -
To import all Airflow objects from an
.envfile to an Astro Deployment, run:astro deployment variable create -d <deployment_id> --load --env .env
If your connections and variables are defined as environment variables on an Astro Deployment, you can export them to a local Airflow environment using the Astro CLI.
-
To export variables from your Deployment, run:
astro deployment variable list --deployment-id <deployment-id> --saveThis command exports your variables to a local file named
.env. The values of secret environment variables will be redacted.
See Set environment variables on Astro.
From the Airflow REST API
You can use the Airflow REST API to import and export connections and variables from a Deployment or local Airflow environment. Note that the Airflow REST API can only access connections and variables that are stored in the Airflow metadata database.
To export connections from any Airflow environment, you can use the List Connections API and Get Connection API.
To export variables from any Airflow environment, you can use the List Variables API and Get Variable API.
To import connections or variables to any Airflow environment, you can use the Create Connection API and Create Variable API respectively.