Best practices for upgrading Astro Runtime on Astro
Astro includes features that make upgrading to the latest version of Astro Runtime easy and, more importantly, safe. When leveraging these features, follow these best practices to ensure that your Deployments remain stable after you upgrade:
- Monitor for upgrade opportunities using Organization dashboards, as well as by following the Astro Runtime maintenance and lifecycle policy.
- Check Upgrade Astro Runtime for advisories on the specific version you're upgrading to.
- Prepare to upgrade safely using upgrade tests.
- In the case of a malfunction after upgrading, revert to your original Astro Runtime version using deploy rollbacks.
Use this document to learn more about each of these best practices for upgrading Astro Runtime.
Best practice guidance
It's best practice to keep your running Astro Runtime versions up-to-date. Astro Runtime upgrades include new Airflow features, as well as bug fixes, security fixes, and improvements to Astro Runtime.
Monitoring for upgrades
Astro users on the Enterprise tier can use Organization dashboards to check whether their currently running Astro Runtime versions are currently supported, as well as how much time is left before they become unsupported. This is especially helpful in cases where your organization has many Deployments to track. See Organization dashboards for steps to access these dashboards.
If you don't have the Enterprise tier of Astro, you can still reference the Astro Runtime maintenance and lifecycle policy to see when you'll need to upgrade your Deployments to a new version of Astro Runtime.
Performing an upgrade
Astro Runtime upgrades can include breaking changes, especially when you upgrade to a new major version. Provider package upgrades in new minor versions of the underlying Airflow package can also cause issues. The Astro CLI has built-in functionality to keep such changes from breaking your DAGs. Astronomer recommends making use of this feature prior to every upgrade.
Use the process described in Upgrade Astro Runtime as the basis for all upgrades. It gives step-by-step guidance on completing an upgrade, as well as version-specific advice. In particular, the following steps should be followed for a smooth upgrade:
-
Pin the provider package versions in your current version of Runtime to ensure a stable upgrade path. This is a simple process involving a single command and, if necessary, modification of
requirements.txtbased on the output. -
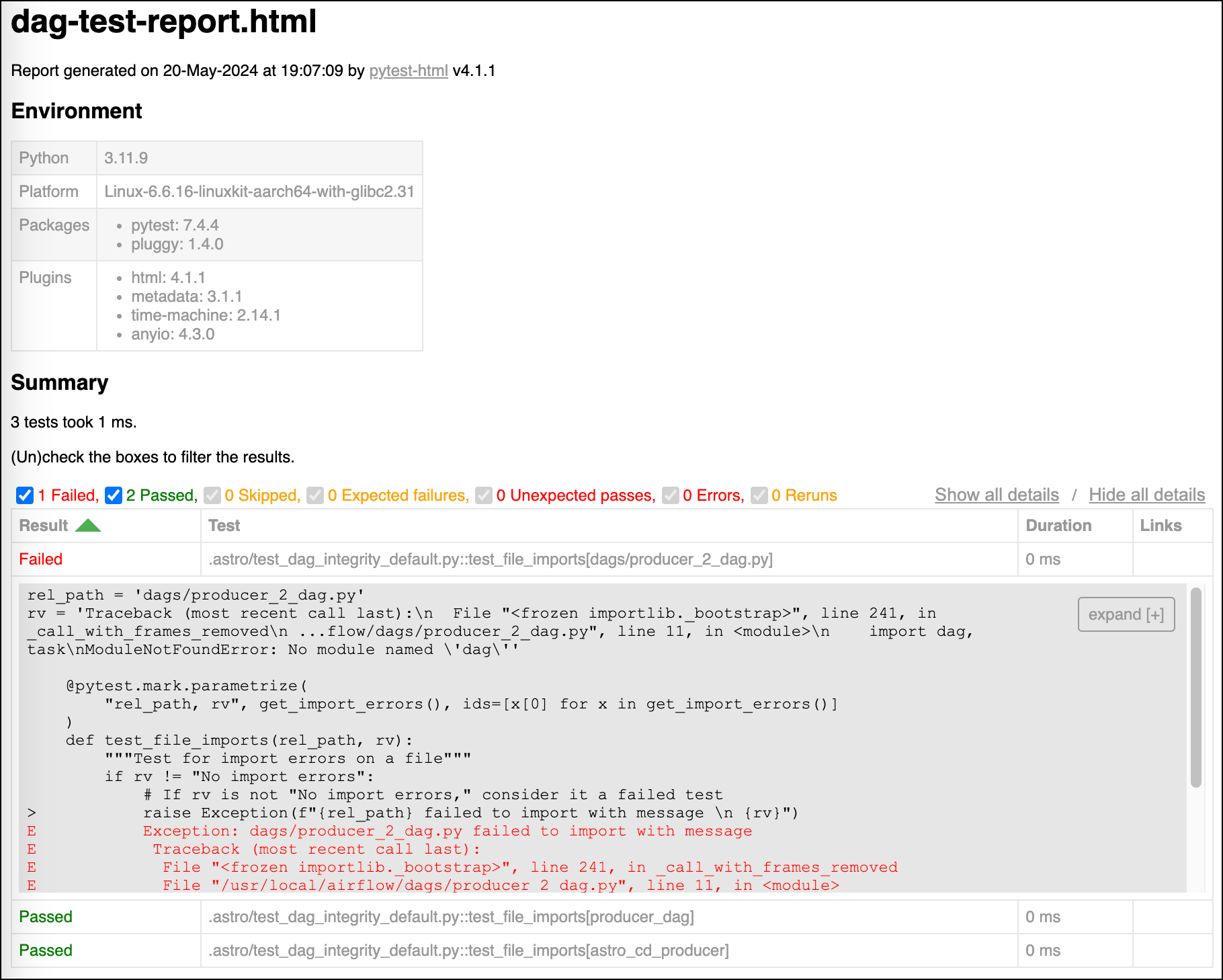
Run upgrade tests to anticipate and address problems. This involves a single command that:
- Compares dependency versions between the current and upgraded environments.
- Checks DAGs in the project against the new Airflow version for errors.
- Runs a DAG parse test with the new Airflow version.
- Produces in new project directory
upgrade-test-<current_version>--<upgraded_version>:- An upgraded
Dockerfile. pip freezeoutput for both versions.- A report with environment metadata and a Results table including any errors logged.
- An upgraded
- A Dependency Compare report listing the upgrades, additions and removals coming in the new Astro runtime version and underlying Airflow package. For example, a "Major Updates" section lists the packages receiving new major versions, and a "Minor Updates" lists the packages receiving new minor versions:
Major Updates:
azure-mgmt-datafactory 6.1.0 >> 7.0.0
Minor Updates:
Flask-Caching 2.1.0 >> 2.2.0
For more details about the upgrade-test command, see Testing your Astro project locally.
Roll back Deployments after a broken upgrade
In the case of emergencies, you can roll back to your previous deploy to downgrade the Astro Runtime version. Astro's rollback functionality is similar to the Git revert command. Rollbacks revert project code only, keeping environment variables and other configuration unchanged. Also, downgrading erases any data related to newer features. For these reasons, Astronomer recommends using rollbacks only as a last resort.
Astronomer recommends triggering Deployment rollbacks only as a last resort for recent deploys that aren't working as expected. Deployment rollbacks can be disruptive, especially if you triggered multiple deploys between your current version and the rollback version. See What happens during a deploy rollback.
The upgrade-test command can also be used to test the current Runtime version against a downgraded version.