Customize Operator Extra Links
Airflow includes plugins for customizing the Airflow UI. One small but impactful customization is adding extra links in the Details view for operators in the UI. These extra links can point to static websites, such as documentation for the operator, or dynamic links created from information during the task instance run.
This tutorial shows how to add both static and dynamic extra links using the AirflowExtraLinkPlugin to existing and custom operators.
After you complete this tutorial, you'll be able to:
- Add a static operator extra link to any operator using an Airflow plugin.
- Modify an existing operator to push an additional value to XCom.
- Add a dynamic operator extra link to any operator using an Airflow plugin.
Time to complete
This tutorial takes approximately 1 hour to complete.
Assumed knowledge
To get the most out of this tutorial, make sure you have an understanding of:
- Navigating an Airflow Project. See Get started with Apache Airflow.
- Airflow Plugins. See Import plugins to Airflow.
- Airflow Connections. See Manage connections in Apache Airflow.
- Intermediate knowledge of Python. See the official Python documentation.
Prerequisites
- The Astro CLI.
Step 1: Create an Astro project
Set up Airflow by creating a new Astro project:
$ mkdir astro-extra-link-tutorial && cd astro-extra-link-tutorial
$ astro dev init
Step 2: Create a DAG using the SimpleHttpOperator
You'll first add a static link to the SimpleHttpOperator which goes to the Mozilla HTTP documentation. This link will appear on every task instance created by this operator.
-
Create a new Python file named
plugin_test_dag.pyin thedagsfolder of your Airflow project. -
Copy and paste the following DAG code into your file:
from airflow.models.dag import DAG
from airflow.providers.http.operators.http import SimpleHttpOperator
from pendulum import datetime
with DAG(
dag_id="plugin_test_dag",
start_date=datetime(2022, 11, 1),
schedule=None,
catchup=False
):
call_api_simple = SimpleHttpOperator(
task_id="call_api_simple",
http_conn_id="random_user_api_conn",
method="GET"
)
This DAG has one SimpleHttpOperator task that posts a GET request to an API as defined in the random_user_api_conn connection.
Step 3: Add a static operator extra link
Create an Airflow plugin to add an extra link to the operator.
-
Create a new Python file named
my_extra_link_plugin.pyin thepluginsfolder of your Airflow project. -
Copy paste the following code into your file.
from airflow.plugins_manager import AirflowPlugin
from airflow.models.baseoperator import BaseOperatorLink
from airflow.providers.http.operators.http import SimpleHttpOperator
# define the extra link
class HTTPDocsLink(BaseOperatorLink):
# name the link button in the UI
name = "HTTP docs"
# add the button to one or more operators
operators = [SimpleHttpOperator]
# provide the link
def get_link(self, operator, *, ti_key=None):
return "https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP"
# define the plugin class
class AirflowExtraLinkPlugin(AirflowPlugin):
name = "extra_link_plugin"
operator_extra_links = [
HTTPDocsLink(),
]
This script accomplishes the following:
- Defines an operator extra link called
HTTPDocsLinkwhich will create an extra link button with the nameHTTP docs. Customize this string to change the name on the button displayed in the UI. - Adds the
SimpleHttpOperatorto the list of operators this extra link will be applied to. You can add as many operators as you'd like, including custom operators. - Defines the
get_link()method which determines the website the operator extra link will link to. You can change this function to any Python function that returns a valid link. See Step 9 for instructions on how to make this link dynamically change between task instances. - Creates an instance of the
AirflowPluginclass which will be automatically picked up by Airflow to install the plugin namedextra_link_pluginin your Airflow instance. - Adds the
HTTPDocsLinkplugin to theextra_link_plugin. You can add several operator extra links to the same Airflow plugin.
Step 4: Add an HTTP connection
-
Run
astro dev startin your Astro project directory to start up Airflow. If your Airflow instance is already running, useastro dev restartto restart it in order to load any changes made in thepluginsfolder. -
Add an HTTP connection called
random_user_api_conntohttp://randomuser.me/api/in the Airflow UI. This API will return data about a randomly generated user persona. Feel free to use a different API, the content returned will not be relevant for this tutorial. Learn more about connections in the Manage connections in Apache Airflow guide.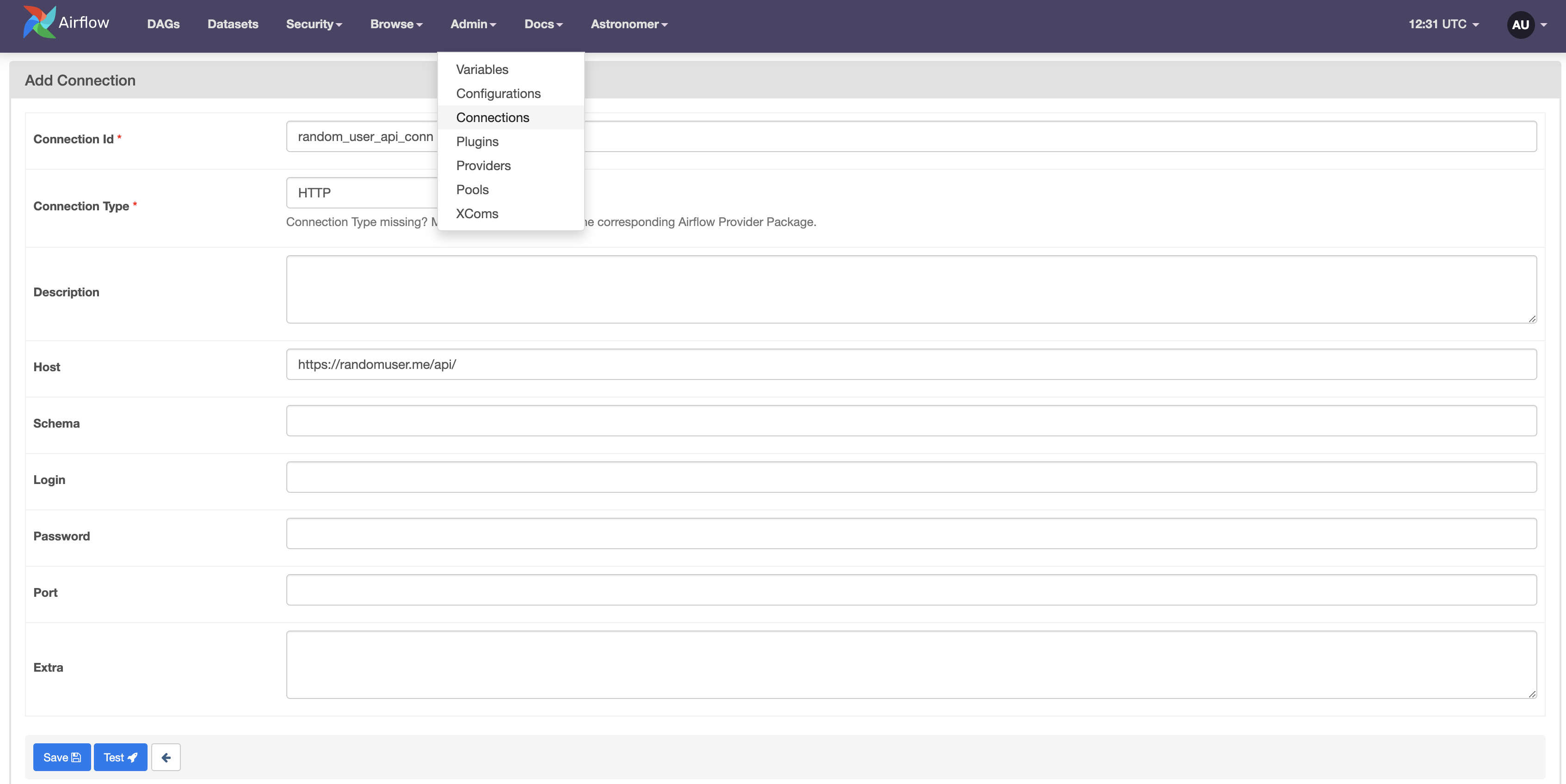
Step 5: Use your static operator extra link
-
Run the
plugins_test_dag. -
In the Grid view, click the green square representing the successful run of the
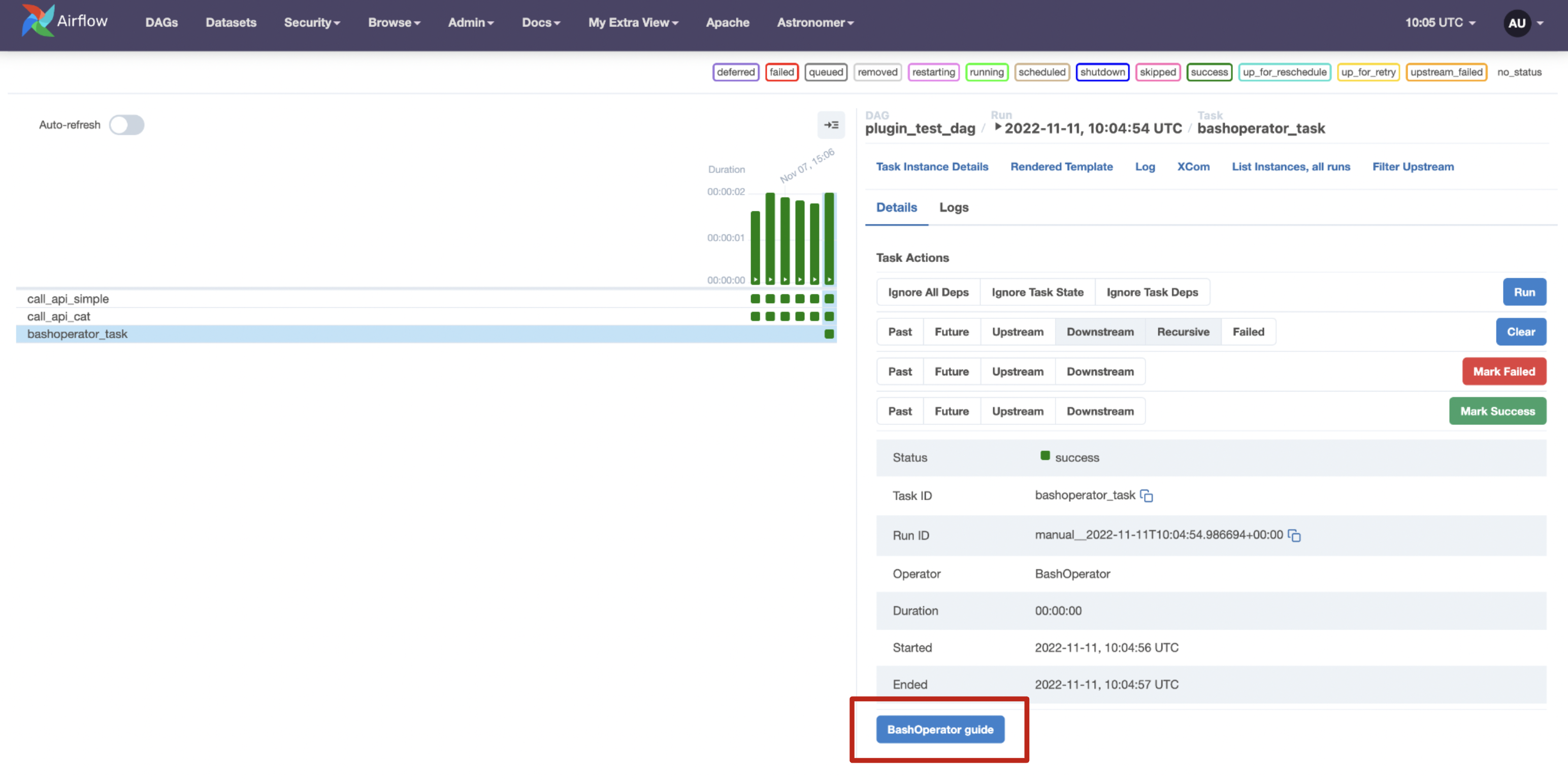
call_api_simpletask. Select the Details tab and scroll down to see the extra link button called HTTP docs.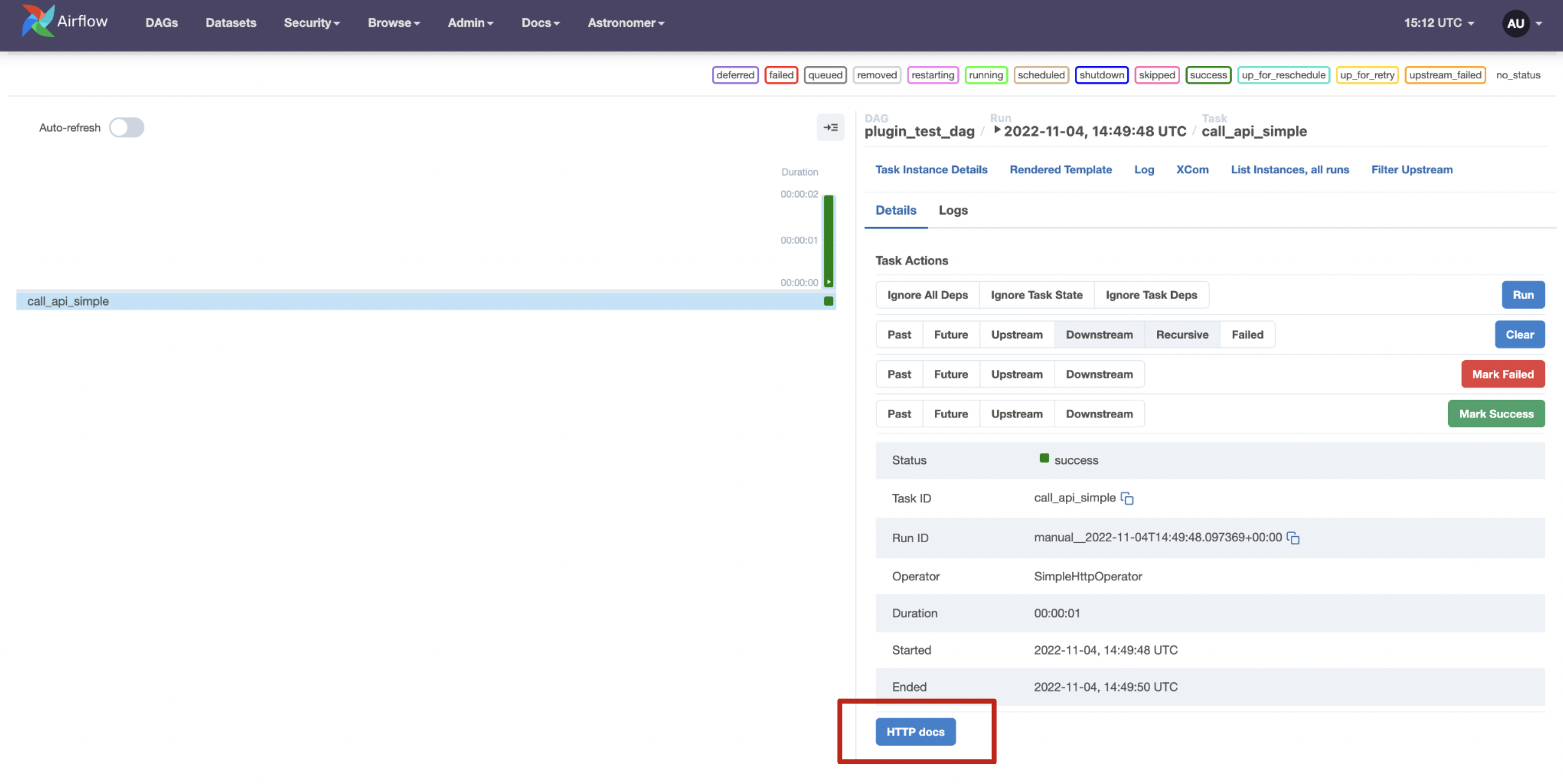
-
Click on the button to visit the HTTP docs on Mozilla.
Step 6: Create a custom operator
Another core feature of extra links is that you can dynamically generate them based on information returned by an operator at run time. The second half of this tutorial will cover how to modify an operator to push the value you need to XComs and retrieve that value for use in an extra link.
-
Create a new file called
cat_http.pyin theincludefolder of your Airflow project. -
Copy the following code into the file.
from airflow.providers.http.operators.http import SimpleHttpOperator
from airflow.providers.http.hooks.http import HttpHook
from airflow.utils.operator_helpers import determine_kwargs
from airflow.exceptions import AirflowException
class CatHttpOperator(SimpleHttpOperator):
# initialize with identical arguments to the parent class
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
def execute(self, context):
http = HttpHook(
self.method,
http_conn_id=self.http_conn_id,
auth_type=self.auth_type,
tcp_keep_alive=self.tcp_keep_alive,
tcp_keep_alive_idle=self.tcp_keep_alive_idle,
tcp_keep_alive_count=self.tcp_keep_alive_count,
tcp_keep_alive_interval=self.tcp_keep_alive_interval,
)
self.log.info("Calling HTTP method")
response = http.run(
self.endpoint, self.data, self.headers, self.extra_options
)
if self.log_response:
self.log.info(response.text)
if self.response_check:
kwargs = determine_kwargs(self.response_check, [response], context)
if not self.response_check(response, **kwargs):
raise AirflowException("Response check returned False.")
if self.response_filter:
kwargs = determine_kwargs(self.response_filter, [response], context)
return self.response_filter(response, **kwargs)
# pushing the HTTP status response to XComs
context["ti"].xcom_push(key="status_code", value=response.status_code)
return response.textThis code defines a custom version of the
SimpleHttpOperatorcalled theCatHttpOperator. This operator has a one-line customization before thereturnstatement of the.execute()method:context["ti"].xcom_push(key="status_code", value=response.status_code).This line pushes the
status_codeattribute of theresponseobject to XComs where it can be called from your plugin. -
Add an empty Python file called
__init__.pyto yourincludefolder. This file enables module imports from the folder.
Step 7: Create a DAG with your custom operator
-
In the
plugin_test_dag.pyfile import theCatHttpOperatorby adding the following import statement at the start of the code:from include.cat_http import CatHttpOperator -
Create a second task in the existing DAG context using the new operator with the code snippet below.
call_api_cat = CatHttpOperator(
task_id="call_api_cat",
http_conn_id="random_user_api_conn",
method="GET"
)
This task will post the same GET request to the API you defined with the connection ID random_user_api_conn as the first task, but this time using the CatHttpOperator.
Step 8: Run your DAG and view modified XComs
-
Run the
plugins_test_dag, which now consists of two tasks. -
Select the latest run of the
call_api_cattask in the Grid view and click on the XCom tab to view XComs returned by this task.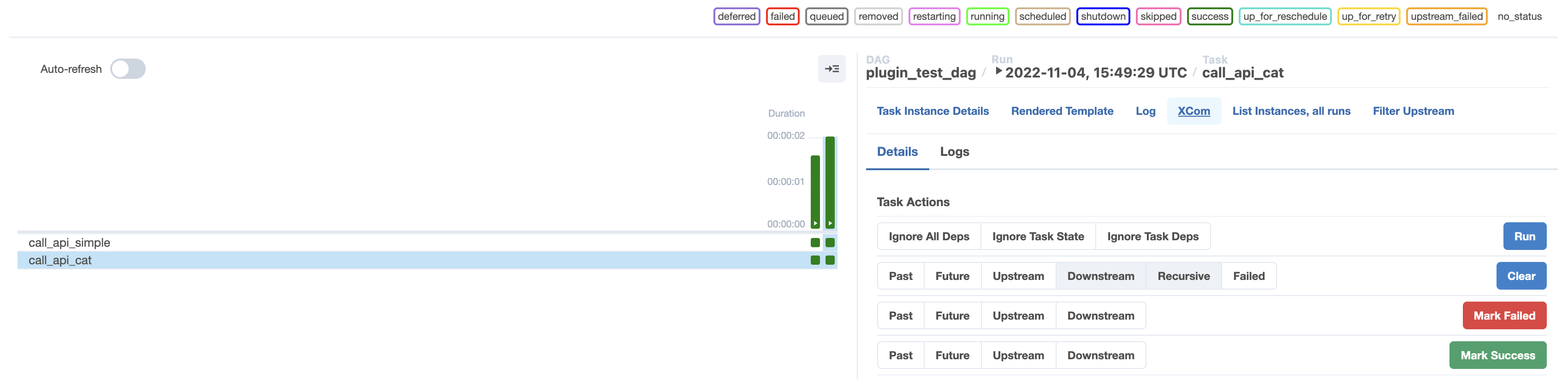
-
Verify that the XCom for this task instance contains an entry for
status_code. In the screenshot below the HTTP status code returned was 200.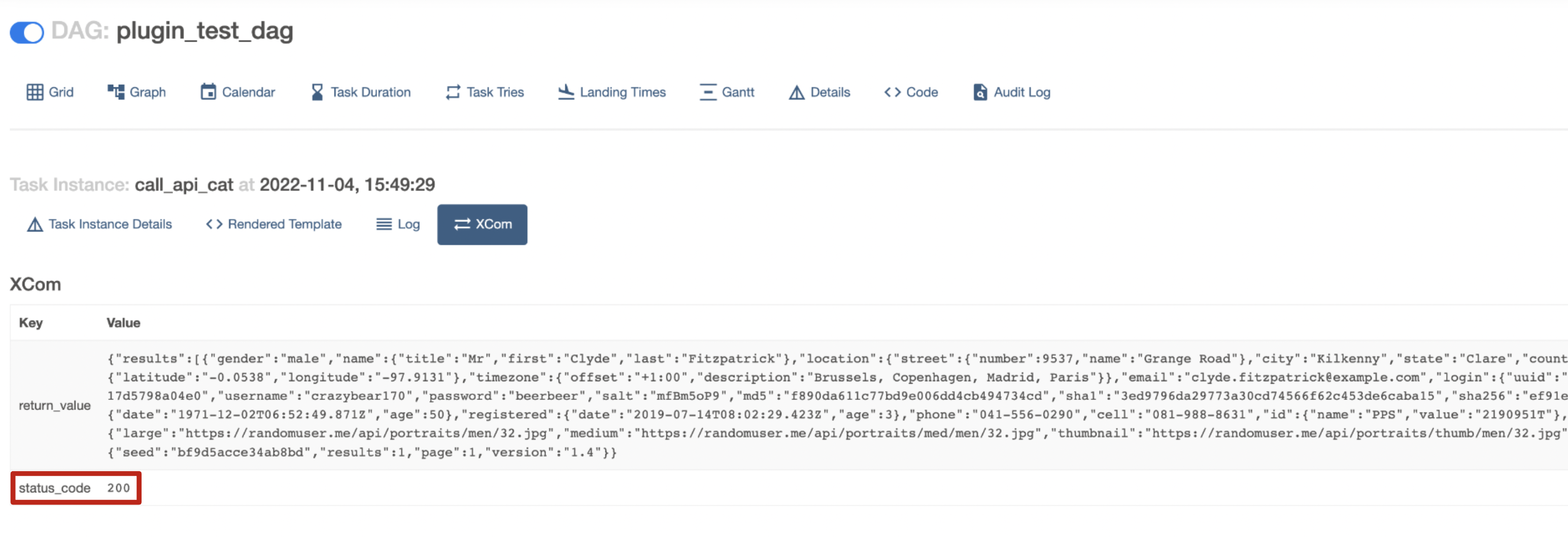
Step 9: Add a dynamic extra link to your custom operator
Next, you will create a dynamic extra link using an Airflow plugin by following these steps:
-
Open
my_extra_link_plugin.pyin yourpluginsfolder. -
Add the following import statements at the start of the file:
from include.cat_http import CatHttpOperator
from airflow.models import XCom -
Copy paste the following code below the definition of the
HTTPDocsLinkclass and above the definition of theAirflowExtraLinkPluginclass.class CatLink(BaseOperatorLink):
# name the link button in the UI
name = "HTTP cat"
# add the button to one or more operators
operators = [CatHttpOperator]
# provide the link
def get_link(self, operator, *, ti_key=None):
status_code = XCom.get_value(key="status_code", ti_key=ti_key) or ""
return f"https://http.cat/{status_code}"This code creates a class called
CatLinkderived fromBaseOperatorLink. The.get_link()method retrieves thestatus_codeyou pushed to XCom and appends it to the HTTP cat Api link. -
Update the
operator_extra_linkslist in theAirflowExtraLinkPluginclass with the newCatLink(). The class should look like this:class AirflowExtraLinkPlugin(AirflowPlugin):
name = "extra_link_plugin"
operator_extra_links = [
CatLink(), # add this line
HTTPDocsLink()
] -
Save the file and restart your Airflow instance with
astro dev restart.
Step 10: See your new extra link in action
Your second extra link has now been added to the CatHttpOperator.
-
In the Airflow UI, run
plugins_test_dagagain. -
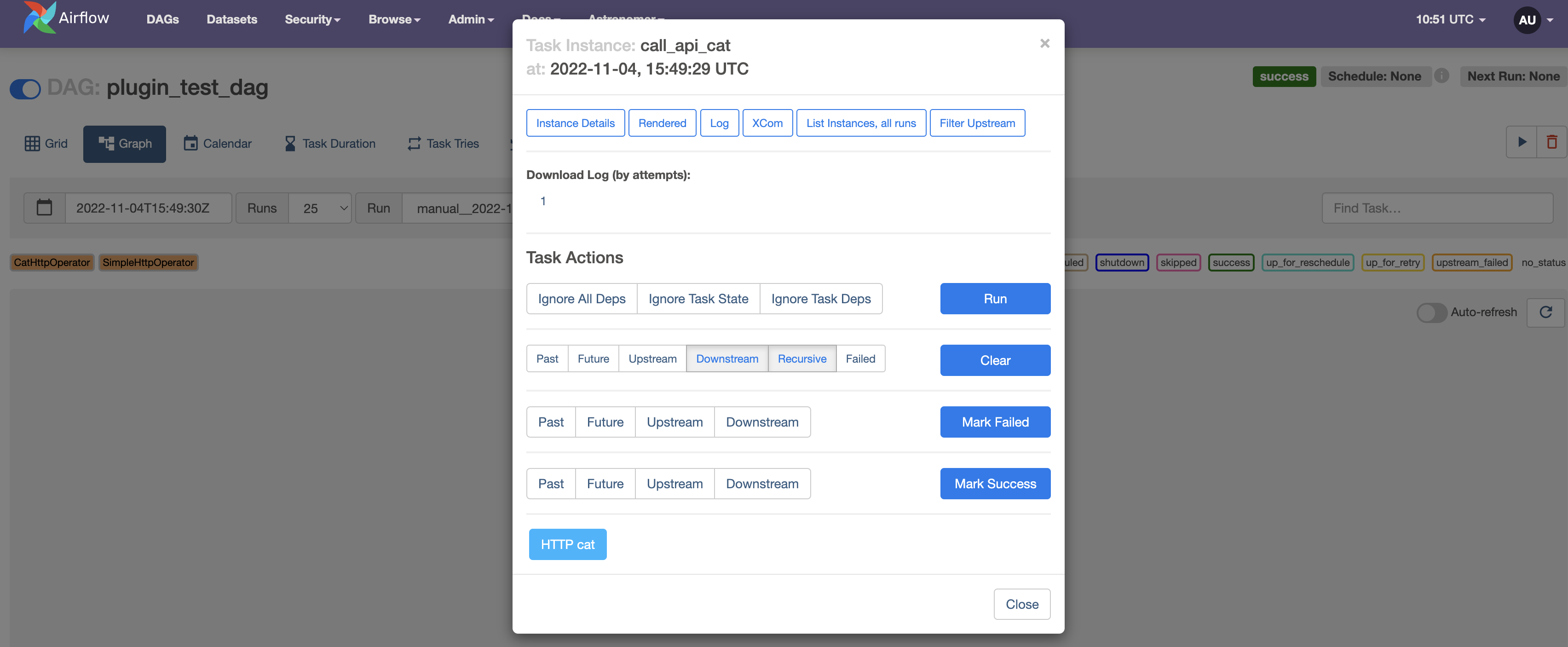
Navigate to the Graph View and click on the
call_api_cattask. -
Click the HTTP Cat button to find the response of your last API call illustrated with a fitting cat.
-
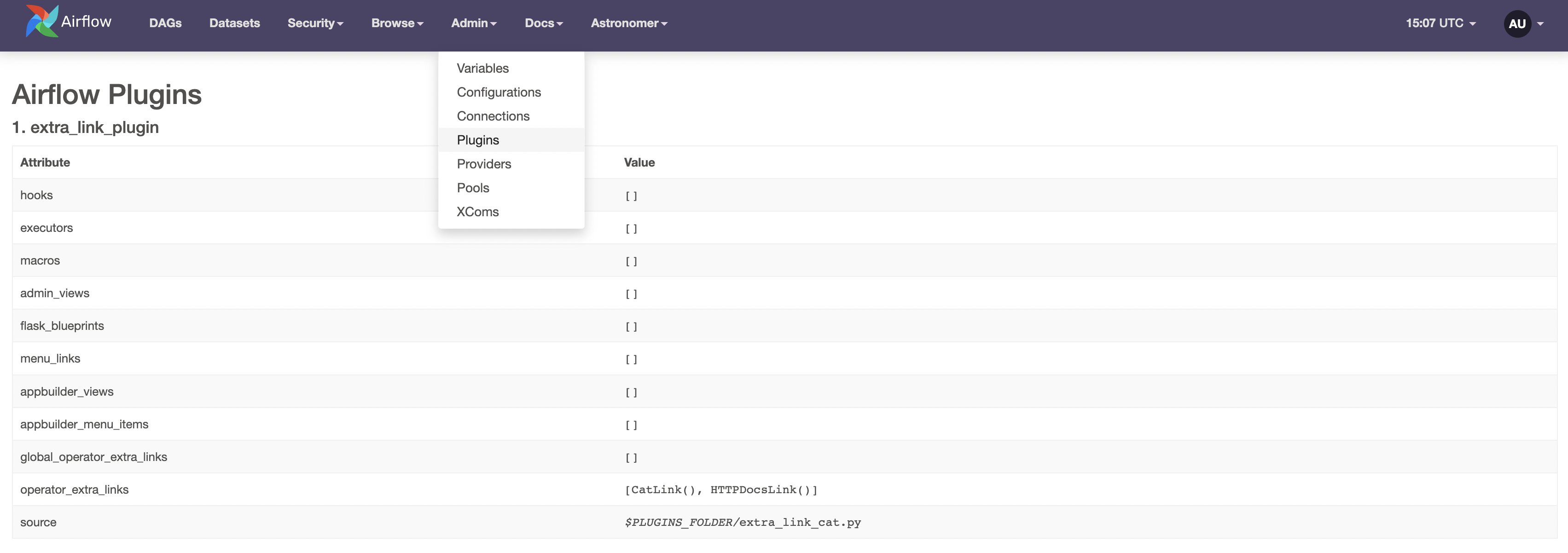
(Optional) See all your plugins listed under Admin -> Plugins.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You added two operator extra links as an Airflow plugin. On the way you also learned how to modify an existing operator to pass an additional value to XCom.
Extra links can be also be added to operators when creating an Airflow provider. If you want to add an operator extra link to a custom operator as part of a provider package, make sure you install it with the rest of the package using a setup.py file or wheels.
In general, adding an operator extra link via plugin as described in this tutorial is easier for use in a limited number of Airflow instances. However, if you are planning to use the extra link in a large number of deployments, consider adding them to an Airflow provider instead.